I2C Address Converter Module SKU: CQRADDR001
Contents
Description
LTC4316 I2C Address Translation Module is a practical I2C bus expansion tool designed to resolve I2C device address conflicts. This module can translate the fixed hardware address of an I2C device into a different communication address, enabling multiple devices with identical addresses to operate simultaneously on the same I2C bus.
Features
- Efficient Address Conflict Solution: Based on the LTC4316IMS chip, it can translate the fixed hardware address of an I2C device into 127 distinct communication addresses, effectively resolving address conflicts on the I2C bus.
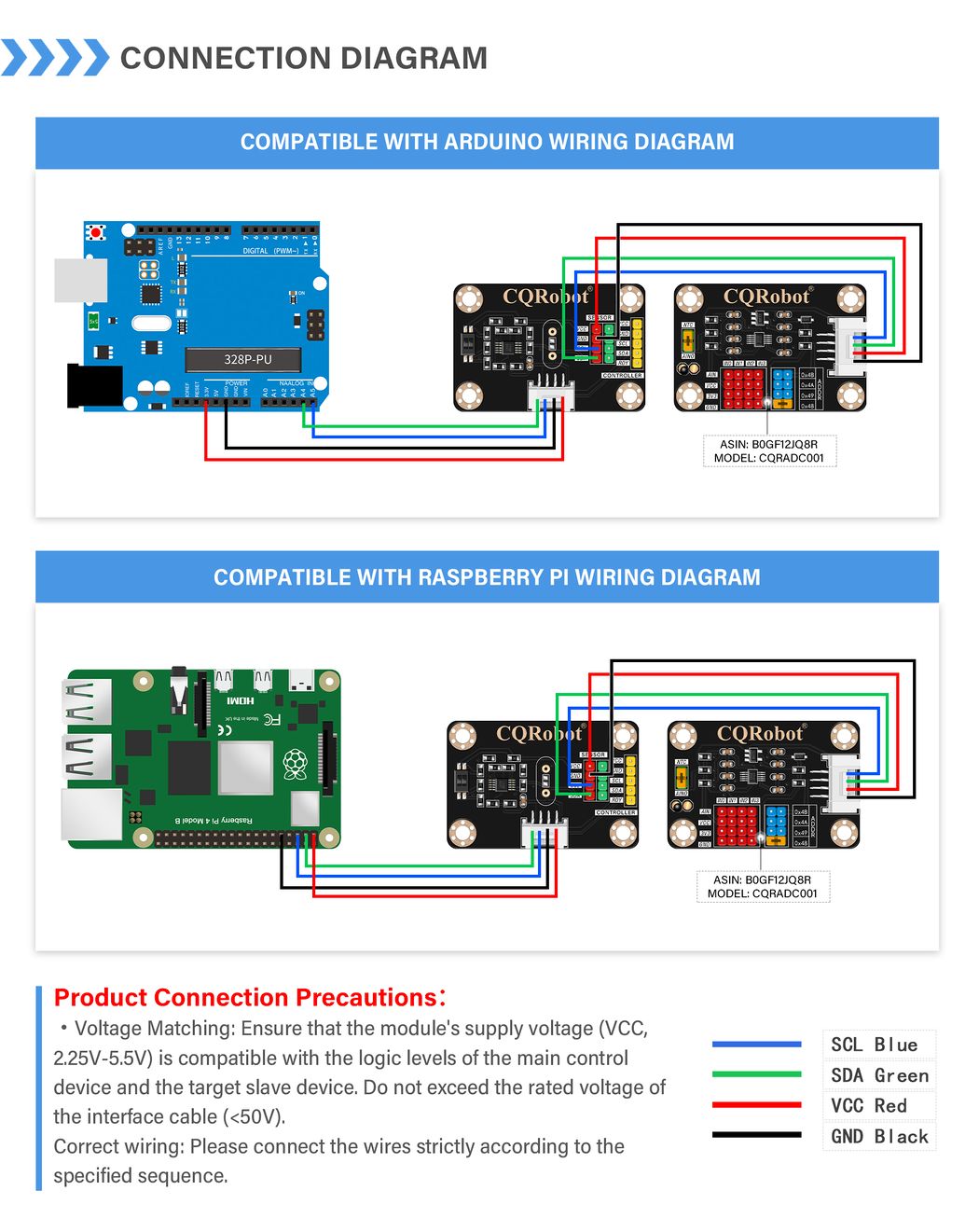
- Wide Voltage Operating Range: Supports power supply voltages from 2.25V to 5.5V, ensuring compatibility with various logic level systems.
- Hardware-Level Transparent Translation: Configures address offsets through a resistive voltage divider network and performs real-time address translation, remaining entirely transparent to both master and slave devices.
- Flexible Address Configuration: Enables independent configuration of the high 3-bit and low 4-bit address offsets via the XORH/XORL pins using resistor voltage division, with support for quick switching via DIP switches.
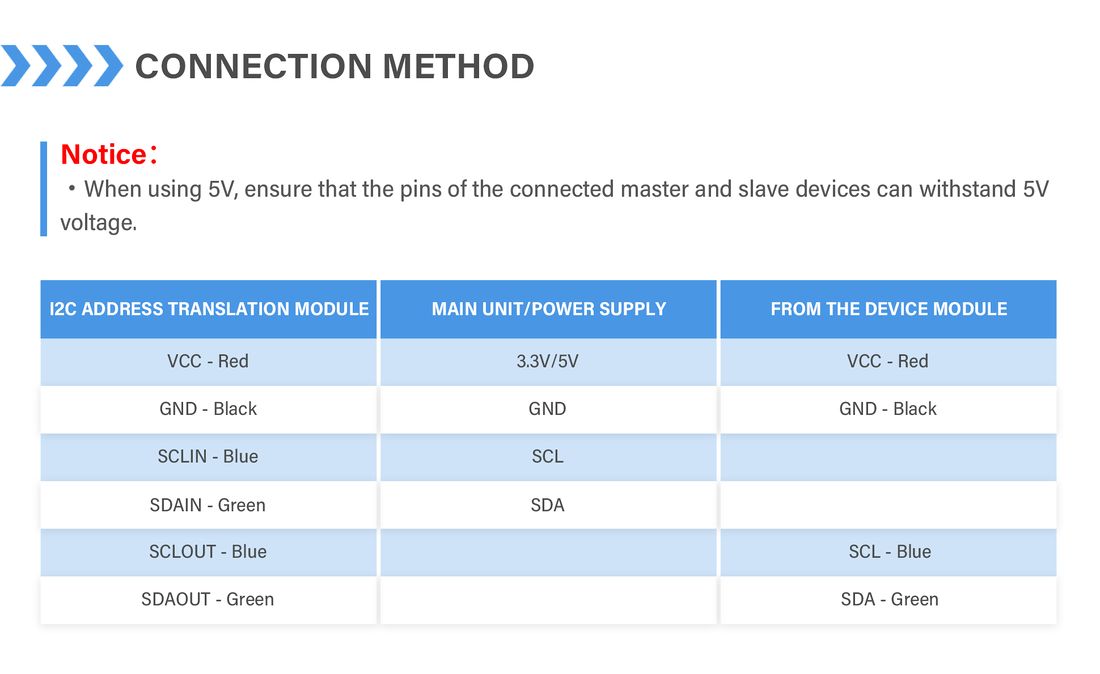
- Industrial-Grade Protection Design: Features separate interfaces for the master side (SCLIN/SDAIN) and slave side (SCLOUT/SDAOUT), providing clear signal flow isolation.
- Standard Interface Compatibility: Equipped with dual interfaces—HY2.0mm 4P connectors and 2.54mm pin headers—for easy connection to various development boards and sensor modules.
Certification Documents
Media:CQRADDR001-CE-Certification.rar
Media:CQRADDR001-FCC-SDOC-Certification.rar
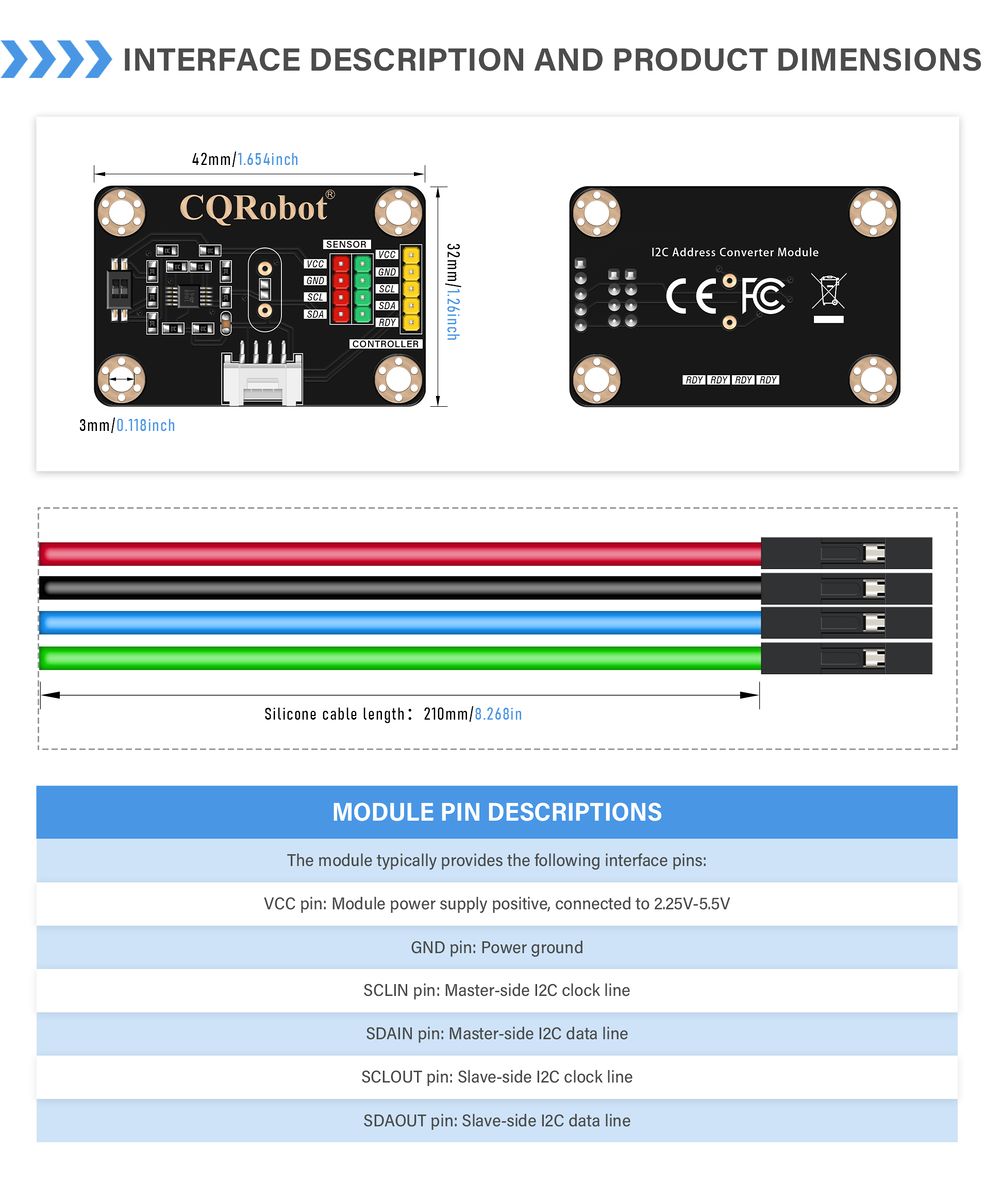
Pin Description and Size
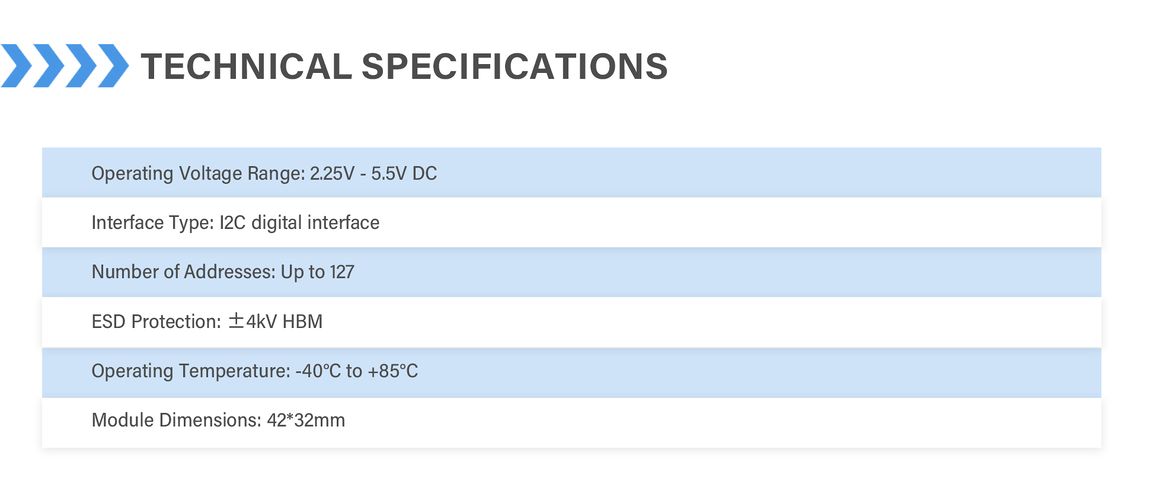
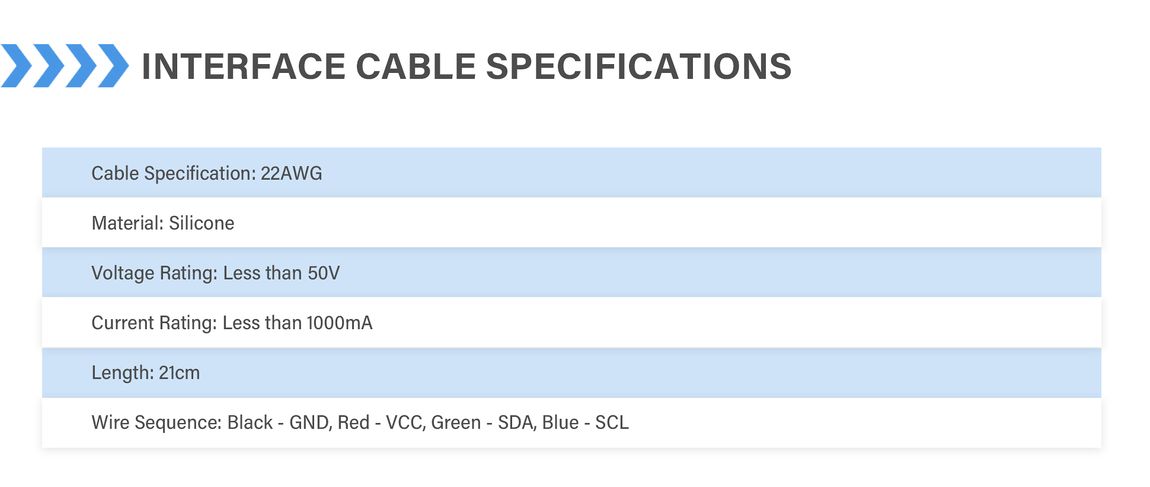
Specification
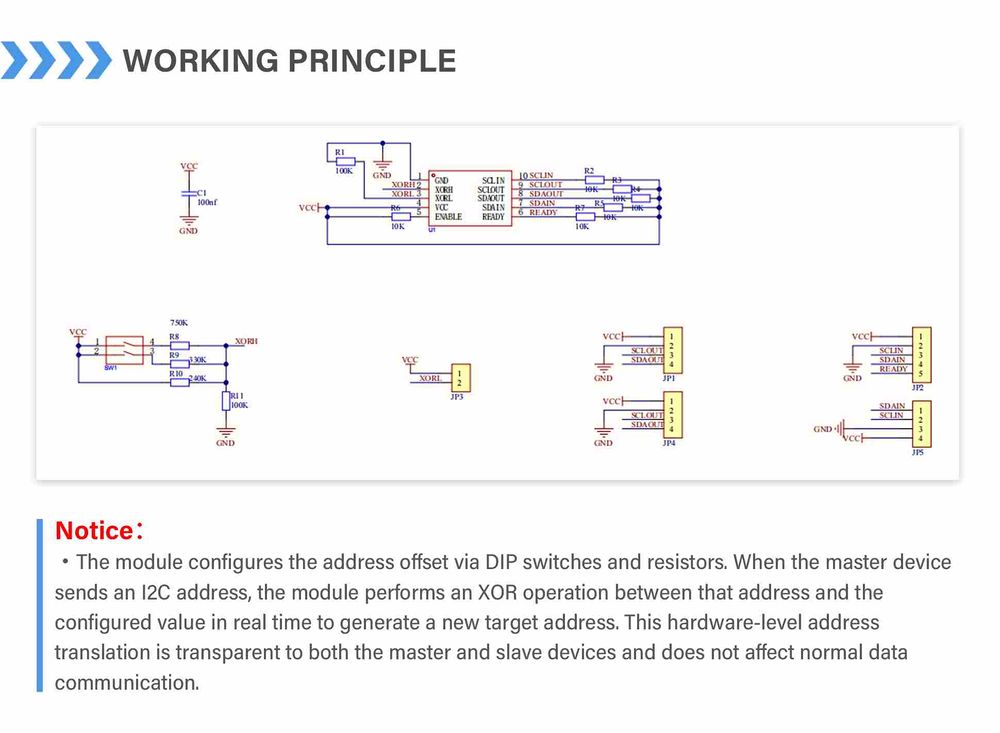
Working Principle
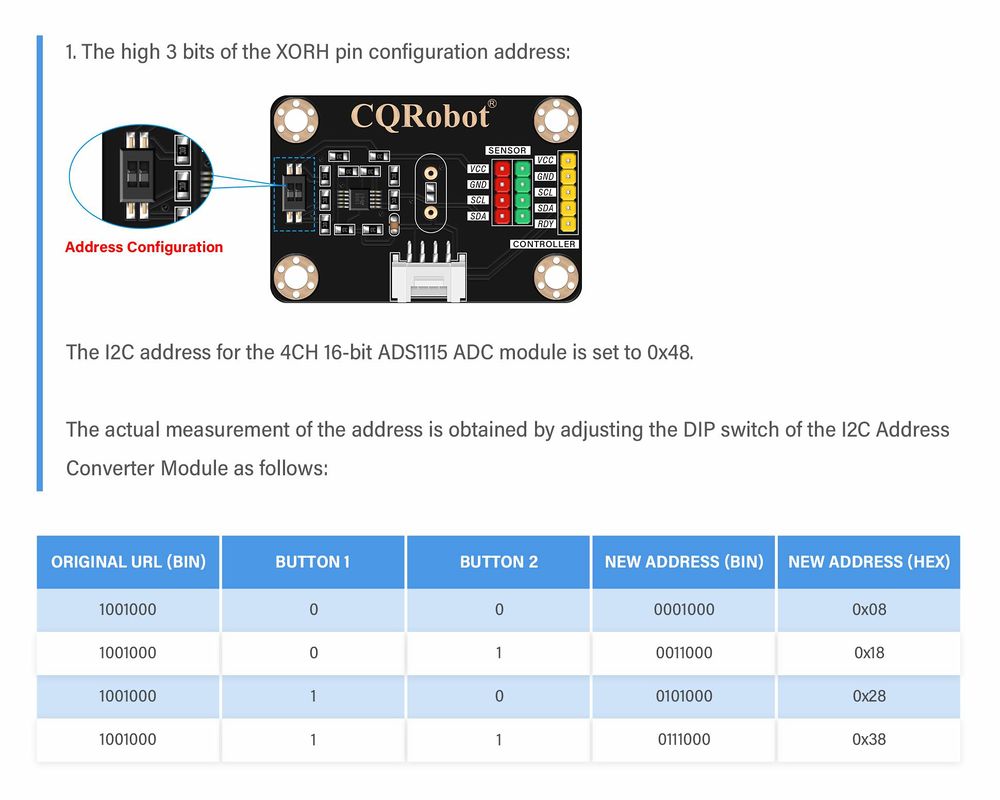
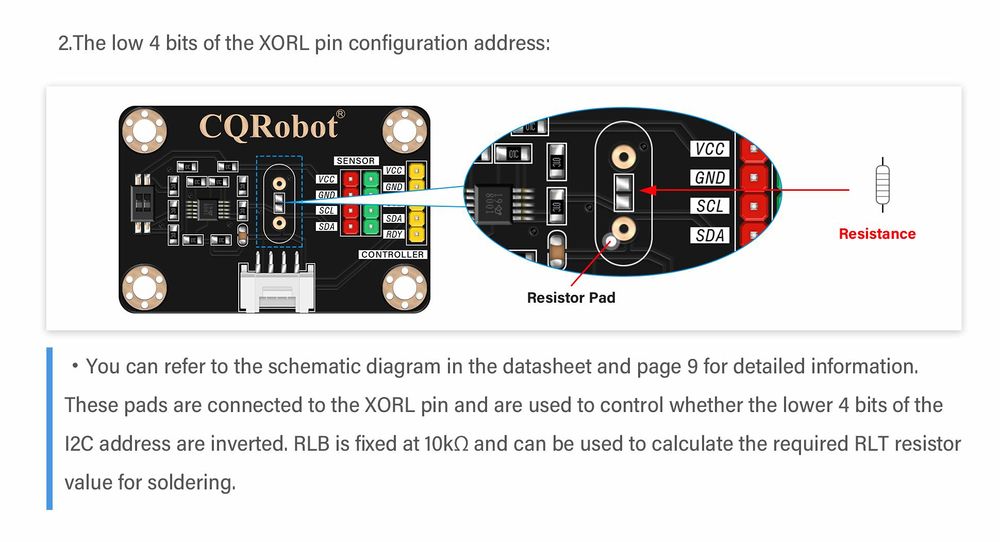
Address Configuration
The module sets the address conversion value through voltage divider resistors at the XORH and XORL pins.
How to determine the resistance of welding resistor:
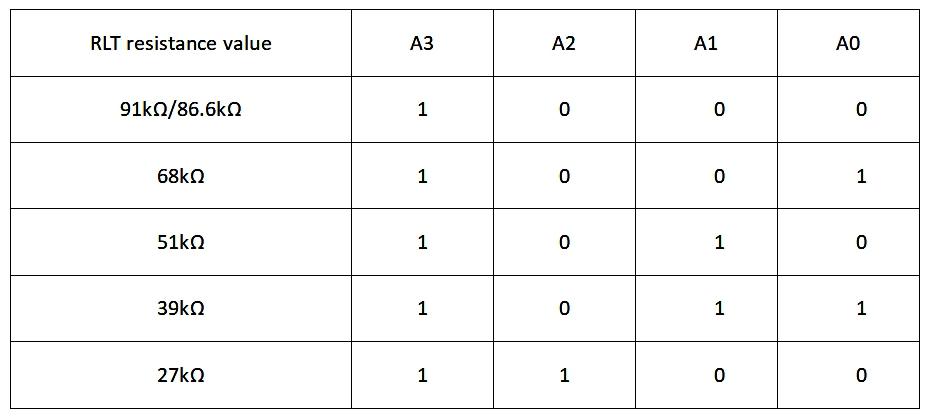
First, based on the data sheet, the module determines whether a specific bit in the I2C address is inverted by the voltage of the XORH or XORL pins (i.e., VXORH or VORL relative to VCC). In Table 2 and 3, a bit value of 1 indicates inversion, while 0 indicates no inversion.
Assuming the VCC is now 5V, set A3-A0 to the 1 0 0 0 mode (A3 inverting while A2-A0 not). This requires VOXRL/VCC to be 0.53125±0.015, general formula: [VCC/(R1+R2)]R1=VXORL.
Given the VCC of 5V and RLB of 100kΩ, the target VXORL should be 0.53125×5V=2.65625V. Substituting all parameters into the formula yields R2 ≈ 88.23529kΩ.
Since this calculated R2 is not the exact common resistance, it should be matched with the closest common resistance value and verified through formula validation.
Under this circumstance, the closest common resistance value to 88.23529kΩ is 86.6kΩ, so VXORL≈2.67953V, or VXORL/VCC≈0.53906. This ratio falls within 0.53125±0.015, making 86.6kΩ a suitable resistance value for RLT.